|
The true measure of the performance of a firm is the value created by a firm over a period of time. However the value of a firm largely depends on the value of beta which denotes the riskiness of the stock of a firm vis-à-vis market. However a firm is largely prone to unsystematic risk which tends to affect individual firms over a large period of time. Over a long period the firm is however able to break free from the shackles of such unsystematic risk. But it must be admitted that the firm continues to suffer from market risk which affects the entire market portfolio. Even MM proposition I and II strongly depend on proper valuation of beta particularly in determining the value of an all equity firm. MM proposition measures value of firm in a world of corporate taxes as
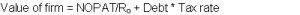
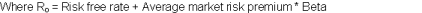
But the question that arises is how should beta measured to determine the actual riskiness of a stock?
One approach usually taken is the stock market approach wherein beta is taken as the sensitivity of stock movement to market indexes beta is measured as:
Beta = COV (i, m)/Variance (m)
Where I = ith stock and m = market movement.
It must be admitted that this method is perhaps one of the easiest to put into action. However this method takes a myopic view of beta as it considers only the past performance of an individual firm vis-à-vis the market. Moreover unsystematic risk is inherent in these methods of beta or firm analysis.
Therefore, the question that must plague any researcher is what is the definite approach to go forward? Perhaps the best measure in such circumstances is the valuation of beta using the bottom up approach which will help to not only to overcome the unsystematic risk but will also help to have stable beta taking into account the perspective of the entire industry. This can be accomplished in a simple five stage process:
Look for comparable firms in the same industry. Preferably the firms should be belonging to the same quartile in the industry. Comparable parameters may be sales, profits, installed capacity etc. Compute the historical beta using stock market index and relevant stock movement of comparable firms. This will give us Beta equity  Unlever the beta using the formula:
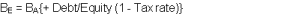
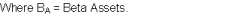
This will give us Beta Assets. Find out the Market value weighted capitalization of Beta Assets using the market values of all the comparable firms mentioned above. This will give us a stable industry Beta Assets thus eliminating unsystematic risk. Finally beta may be levered using the formula mentioned in (3) to get back Beta assets of individual firms.
Next
* Contributed by -
Pinak Rudra Bhattacharyya,
Ist Year,
IMT Ghaziabad.
|