|
Part - I
Abstract
Securitization has emerged globally as an important technique for bundling assets and segregating risks into marketable securities. This paper discusses the present nascent state of the securitization market in India, its potential and attempts to identify what needs to be done by various stakeholders in this market for securitization to grow to its full potential in India.
Introduction
Securitization is the process of pooling and packaging Financial Assets, usually relatively illiquid, into liquid marketable securities. Securitization allows an entity to assign (i.e. sell) its interest in a pool of financial assets (and the underlying security) to other entities. Figure 1 below presents the structure of a Collateralized Loan Obligation (CLO) *, a typical securitization transaction.
Figure 1: Sample CLO structure
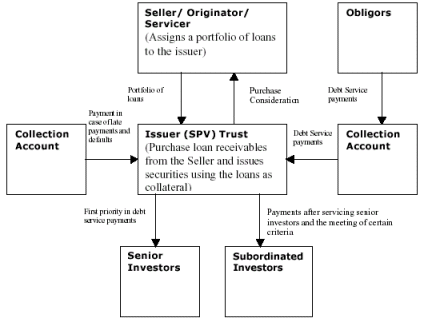
In the above CLO transaction, the originator packages a pool of loans and assigns his interest therein, including the underlying security, to a bankruptcy remote & tax neutral entity which, in turn, issues securities to investors. The idea of such an exercise is to completely transfer the interest in pool of loans to the investors (a "true sale") and achieve a rating higher than that of the Originator **.
Next
* CLOs are securities backed or collateralized by a diversified portfolio of secured or unsecured loans made to a variety of corporate commercial and industrial loan customers of one or more lending banks.
** Structured rating analytical criteria focus on how much credit enhancement is needed to achieve such a
rating, and accompanying legal criteria focus on isolation of the assets from the credit risk of the seller.
Written by V. Sridhar, PGP 2002, IIM Calcutta.
Contributed by Varun Goenka, Diploma in Business Finance Economics, ICFAI.
|